Professional Guide to the Properties and Material Selection of PVC-coated Steel Wire Rope
This article will delve into the core characteristics of PCSR (Polymer Coated Steel Wire Rope) and the professional selection principles for different coating materials from three dimensions: materials science, mechanical behavior, and environmental adaptability.

I. Core Engineering Characteristics of PCSR
The performance of PCSR is the result of the coupling between the inherent strength of the steel wire rope and the functionality of the polymer shell.
1.1. Superior Corrosion Protection and Extended Lifespan
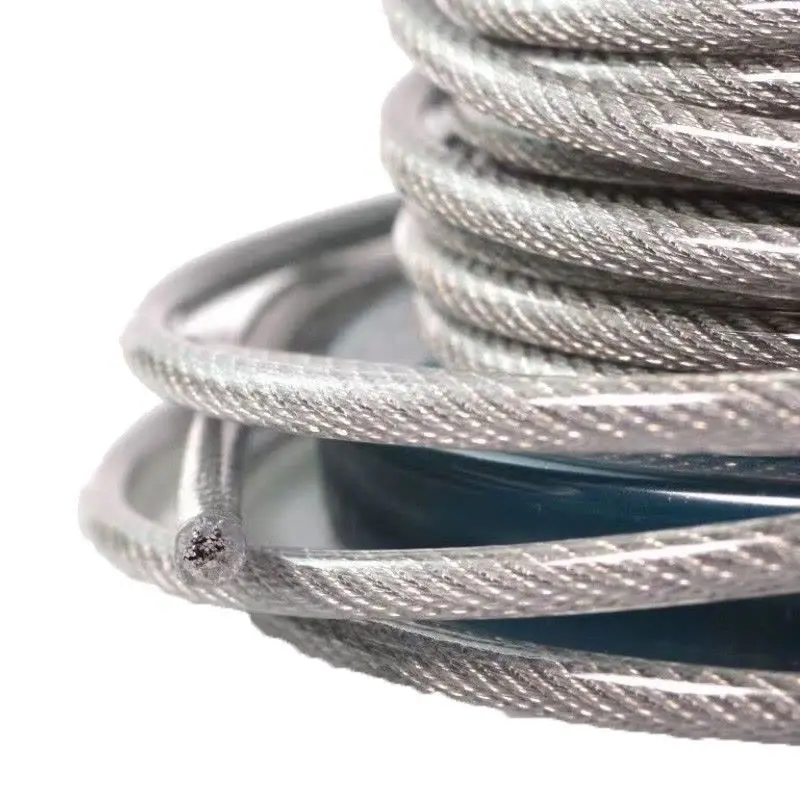
This is the most significant value proposition of PCSR. The polymer shell provides an effective physical barrier, isolating the steel wire rope matrix from external moisture, salt spray, chemicals, and contaminants.
Upgraded Sacrificial Protection Mechanism: If the base steel wire rope itself is galvanized (such as EG or HDG), the plastic coating acts as a second line of defense, significantly extending the sacrificial anodic protection life of the zinc layer, thereby extending the overall corrosion life of the steel wire rope several times over.
Cleanliness Maintenance: The smooth surface of the coating is easy to clean, preventing contaminants and particles from penetrating into the steel rope and maintaining the rope's original lubrication state.
1.2. Improved Dynamic Mechanical Behavior
The outer polymer coating plays a unique buffering role in dynamic applications. Noise Reduction and Vibration Damping: The elastic coating effectively absorbs and dampens vibrations and noise generated by the wire rope during high-speed operation, improving system smoothness and comfort.
Surrounding Component Protection: The coating prevents direct steel-to-steel contact between the wire rope and pulleys, guide rails, or other structural components, significantly reducing wear on contact parts (such as nylon pulleys).
Resistance to Bending Fatigue: The coating can slightly buffer stress between the steel strands, helping the wire rope resist fretting wear to some extent. However, if the coating is too thick or too hard, it may inhibit the flexibility of the wire rope.
1.3. Enhanced Safety and Functionality
Visual Identification: The coating can be customized in color for safety warnings, zoning, or aesthetic matching (e.g., construction cables).
Improved Tactile Feel: Provides a smooth, burr-free surface, enhancing operational safety, suitable for fitness equipment and control handles.
Sealing: Especially with a tight extrusion process, it prevents internal lubricant loss.
II. Professional Comparison of Core Coating Polymer Materials
The functionality of PCSR mainly depends on the chemical structure and physical properties of the outer polymer material.
| Coating materials | Abbreviation | Core Features | Typical application scenarios |
| Polyvinyl chloride | PVC | Economical and highly flexible. Good water and oil resistance; easy to color; however, it has poor temperature resistance and is prone to aging and becoming brittle with long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. | Indoor fitness equipment, basic control cables, binding purposes. |
| Polyethylene | PE | It has excellent weather resistance and chemical resistance. It also has good electrical insulation properties; low density and good low-temperature resistance; however, its hardness is generally lower than that of nylon. | Outdoor guy wires, agricultural applications, and cable auxiliary support. |
| Polyurethane | PU | Excellent abrasion resistance and high elasticity. High tear strength and good cushioning against impact loads. Higher cost, classified as a high-performance coating. | High-speed automated equipment, buffer cables, and industrial environments requiring high wear resistance. |
| Nylon (polyamide) | PA | Excellent mechanical strength and wear resistance. Low coefficient of friction and better temperature resistance than PVC; among all common coatings, it has the strongest resistance to repeated friction. | Industrial automation, slings, and dynamic applications with high requirements for service life and reliability. |
III. Engineering Selection Strategy and Considerations
Selecting a suitable PCSR requires a comprehensive evaluation based on the operating environment, load patterns, and expected lifespan.
3.1. Environmental Corrosion Class
Humid/Salt Spray Environments: PE or PU coatings should be preferred due to their lower water vapor permeability and superior chemical stability compared to PVC. The base steel rope must be HDG or stainless steel (SS304/SS316).
UV Exposure: For long-term outdoor use, PE or PVC/PU materials with added UV stabilizers must be selected to prevent polymer photodegradation, which can lead to cracking and peeling.
3.2. Dynamic Loading and Abrasion
High-Frequency/High-Friction Cycling: For example, guide ropes or slings in automated production lines must be coated with **nylon (PA) or polyurethane (PU)**. These two materials can withstand higher surface stresses and are less prone to failure due to localized frictional heating.
Low-frequency/static cables: If the primary function is isolation and decoration, such as in building railings, PVC can be chosen to reduce costs.
3.3. Coating Thickness and Flexibility Matching
High Flexibility Requirements: When the wire rope needs to be repeatedly wound around small-diameter pulleys (such as in fitness equipment), a thin-walled coating (e.g., 0.5mm - 1.0mm) should be selected, and high-flexibility PVC should be preferred to avoid the coating hardness inhibiting the bending fatigue life of the steel rope.
High Compression/Cushioning Requirements: If the rope needs to withstand a certain amount of compression or act as end cushioning, a thick-walled PU coating should be selected to provide greater elastic deformation space.
IV. Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
The performance of PCSR depends not only on the material but also on the quality of the coating process.
1.Extrusion Process: Modern PCSR mainly uses extrusion. High-quality extrusion must ensure that a dense, bubble-free coating layer is formed between the polymer and the steel rope, preventing internal air or moisture retention and avoiding "hollow" phenomena.
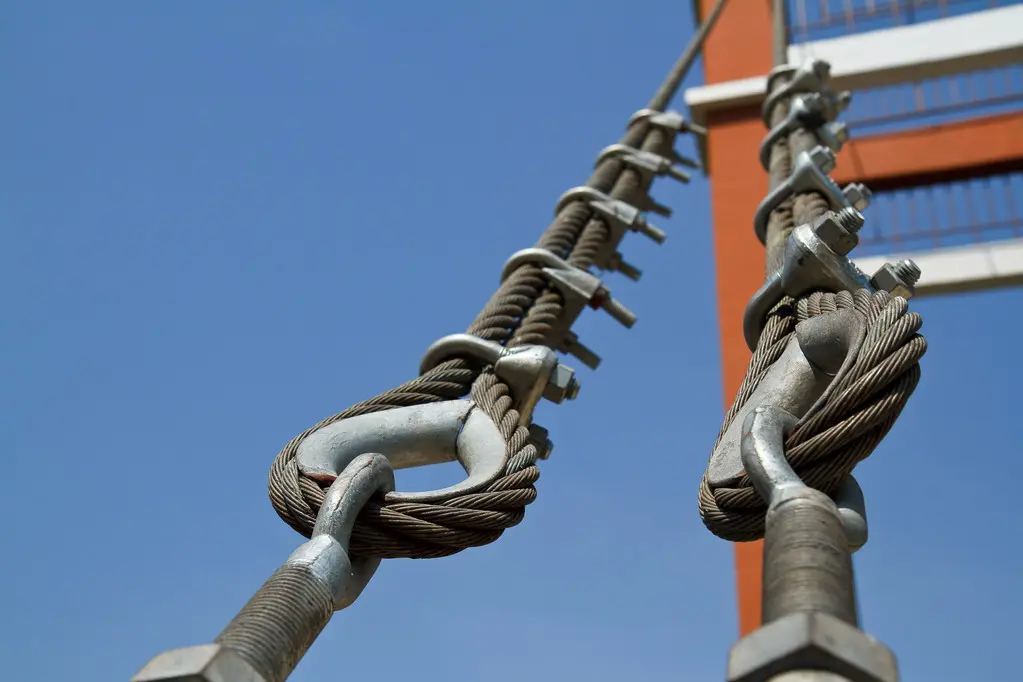
2.Adhesive/Primer: For demanding applications, a special chemical adhesive may be applied to the steel rope surface to enhance the interfacial adhesion between the polymer coating and the galvanized layer or steel substrate, preventing axial slippage or radial detachment of the coating during use.
3.Dimensional Tolerances: Controlling the final outer diameter tolerances is crucial to ensuring a precise fit between the PCSR and its matching pulley grooves or connectors.
Conclusion
Selecting PCSRs is a typical multi-objective optimization problem, requiring the finding of the optimal balance between cost, corrosion life, and mechanical fatigue performance. Engineers should prioritize materials with excellent abrasion resistance (PA/PU) for dynamic load-bearing based on the project's actual corrosion level, and select materials with high cost-effectiveness and good moisture barrier properties (PE/PVC) for static protection and aesthetic requirements. Only by precisely matching the properties of the coating materials to the requirements of the application environment can the engineering value of PCSRs be maximized.