Choosing the right marine anchor chain is crucial for the safety and stability of any vessel
It's not a one-size-fits-all decision, as several factors come into play. Here's a breakdown of what to consider:

Key Factors in Selecting Marine Anchor Chains
1. Vessel Size and Type
The most fundamental factor is the size and type of your vessel. Larger, heavier ships require stronger, more robust anchor chains. The displacement of your boat is a primary determinant of the required chain strength. Consult classification society rules (like ABS, DNV, LR) or naval architect recommendations specific to your vessel's category (e.g., cargo ship, tanker, yacht, tugboat).
2. Mooring Conditions
Consider the typical mooring environments you'll encounter. This includes:
Water depth: Deeper waters require longer chain lengths.
Seabed type: Chains perform differently on various seabeds (mud, sand, rock). This can influence the anchoring system as a whole, but the chain's integrity is paramount.
Expected weather and sea states: If you frequently operate in areas prone to strong winds, currents, or heavy seas, you'll need a chain with a higher breaking strength and possibly a longer scope (ratio of chain length to water depth).
3. Chain Specifications and Standards
Material: Most marine anchor chains are made from high-strength, heat-treated alloy steel for maximum durability and resistance to corrosion and abrasion.
Link size (diameter): This is directly related to the chain's strength. Larger diameters mean greater strength.
Grade of chain: Anchor chains are often graded (e.g., Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3, AM1, AM2, AM3). Higher grades offer increased strength and impact resistance, crucial for demanding conditions. Grade 3 and AM3 chains are typically used for offshore applications and vessels operating in harsh environments.
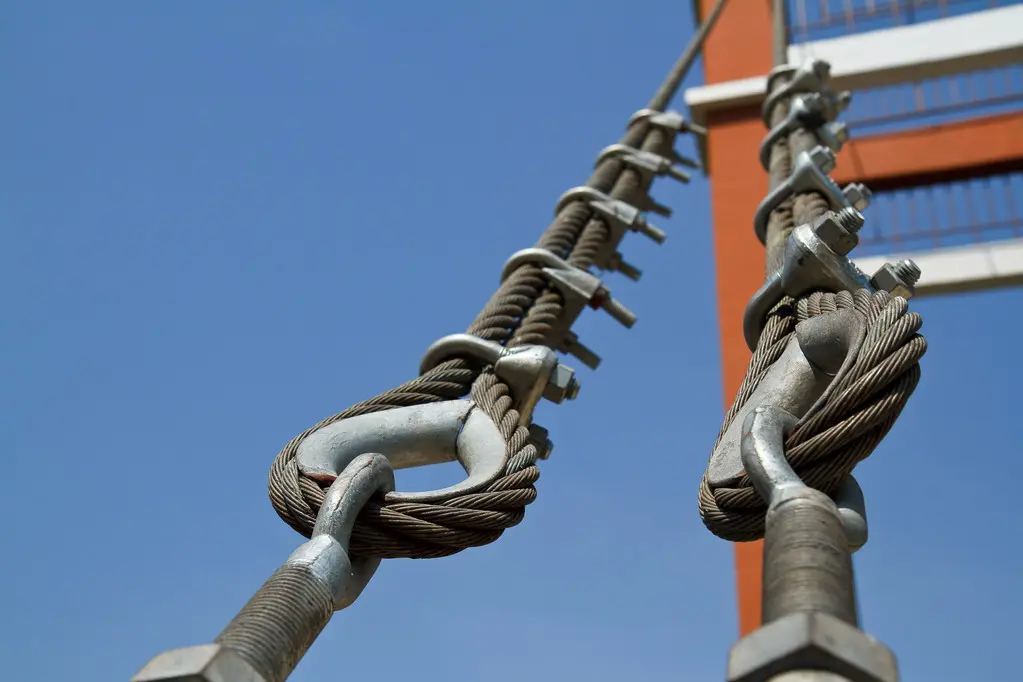
Breaking Strength: This is the minimum force required to break the chain. It's a critical safety parameter.
Working Load Limit (WLL): This is the maximum load the chain can safely handle during operation. It's always significantly lower than the breaking strength.
Certifications: Ensure the chain is certified by a recognized classification society. This guarantees it meets stringent quality and safety standards.
4. Chain Length and Scope
The length of the anchor chain is as important as its strength. The principle of scope dictates the relationship between the length of the chain deployed and the water depth. A typical scope for anchoring in moderate conditions is 5:1 or 7:1 (chain length to water depth). In severe conditions, a longer scope may be necessary. Always carry enough chain to achieve the required scope in the deepest anchorage you anticipate using.
5. Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Anchor chains are constantly exposed to saltwater, which is highly corrosive. Look for chains with good corrosion resistance. Regular inspection, cleaning, and maintenance are vital to prolong the chain's life and ensure its integrity. This includes checking for wear, corrosion, and damaged links.
6. Manufacturer Reputation and Warranty
Choose reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality marine anchor chains. A good warranty can provide peace of mind.
Recommendations for Selection
Consult the Classification Society: If your vessel is classed, always refer to the rules and recommendations of your classification society.
Seek Professional Advice: Naval architects or experienced marine equipment Suppliers can provide expert guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Don't Compromise on Quality: The anchor chain is a critical safety component. It's not an area to cut costs. Investing in a high-quality, properly specified chain is an investment in the safety of your vessel and crew.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and select the most appropriate marine anchor chain for your vessel's operational requirements.