The Secret to the Longevity of Steel Cables: Exploring How Coating Technology Reshapes Their Service Life
Lifecycle Protection for Steel Cables: In-Depth Analysis of the Key Roles of Protective Treatments and Outer Sheaths.
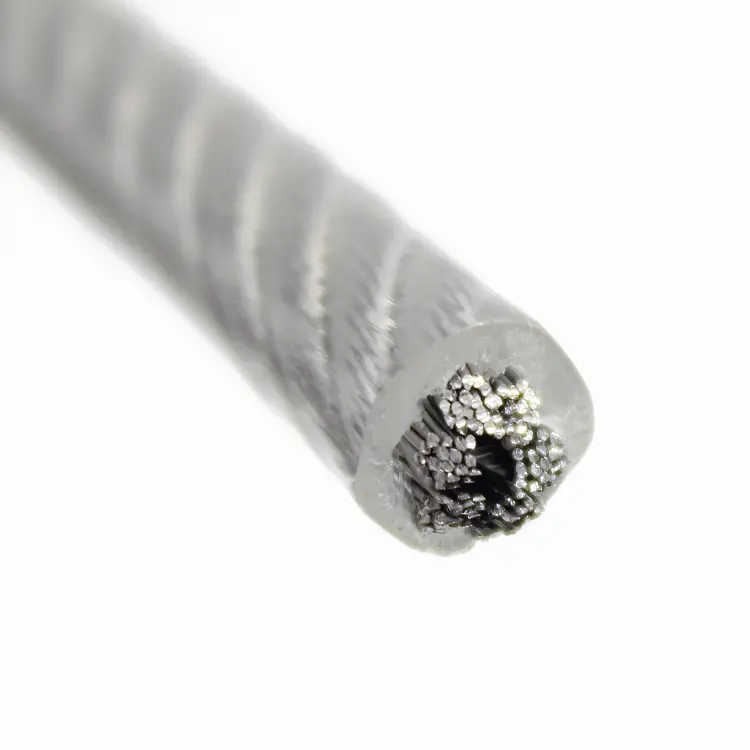

The true durability of steel cables goes far beyond their diameter and nominal tensile strength. The core factors determining a steel cable's lifespan, operational safety, and environmental adaptability lie in the selection of its surface protective treatment and outer sheath materials. Choosing the right protection solution can significantly reduce maintenance investment and downtime, and effectively prevent potential structural failures under harsh operating conditions.
This article aims to clarify the technical differences between two main protective methods—"surface treatment" and "outer sheath"—to guide you in making the right decisions in critical applications, and to compare the performance of galvanized and stainless steel finishes in various harsh environments.
1. Conceptual Clarification: The Essential Difference Between Surface Treatment and Outer Sheaths
In the field of steel cable protection, **surface treatment (finishing) and outer sheath (coating)** play distinctly different roles. Understanding their differences is the first step in ensuring the long-term reliability of steel cables.
(1) Surface Treatment (Metallic Finish): The Structure's "Inherent" Barrier
Surface treatment directly modifies the steel wires that make up the cable through chemical or electrochemical processes. It forms the first line of defense against corrosion and chemical attack.
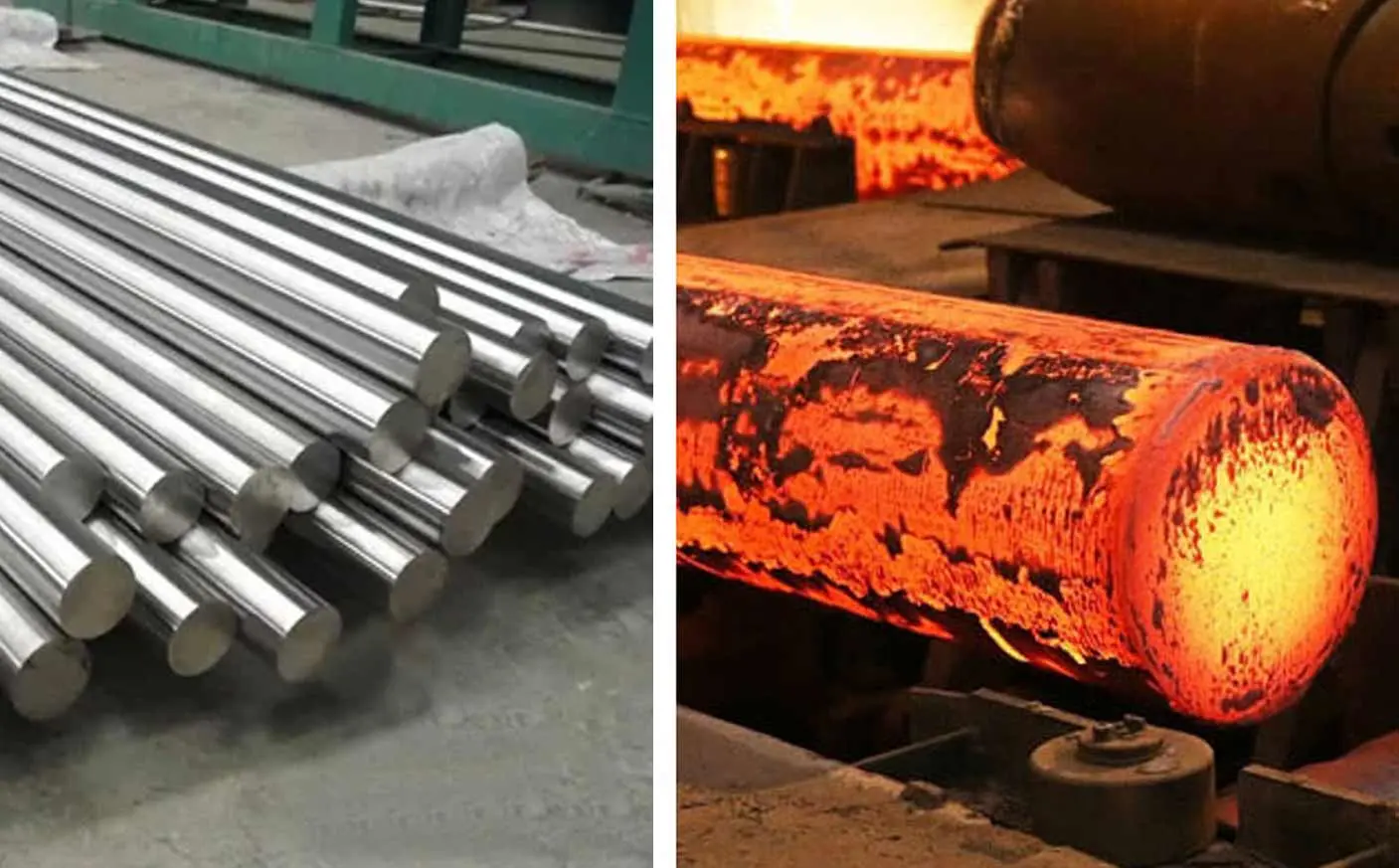
Representative Technologies: Galvanized (hot-dip or electrolytic), Stainless Steel (e.g., AISI 304, 316 grades).
Core Functions: Improves the inherent durability of the steel, prevents oxidation and rust, and enhances structural durability in outdoor or highly corrosive industrial environments.
Application Scenarios: Recommended for applications in humid, salt spray, and frequent chemical exposure environments, including ports, marine engineering, and heavy industrial areas.
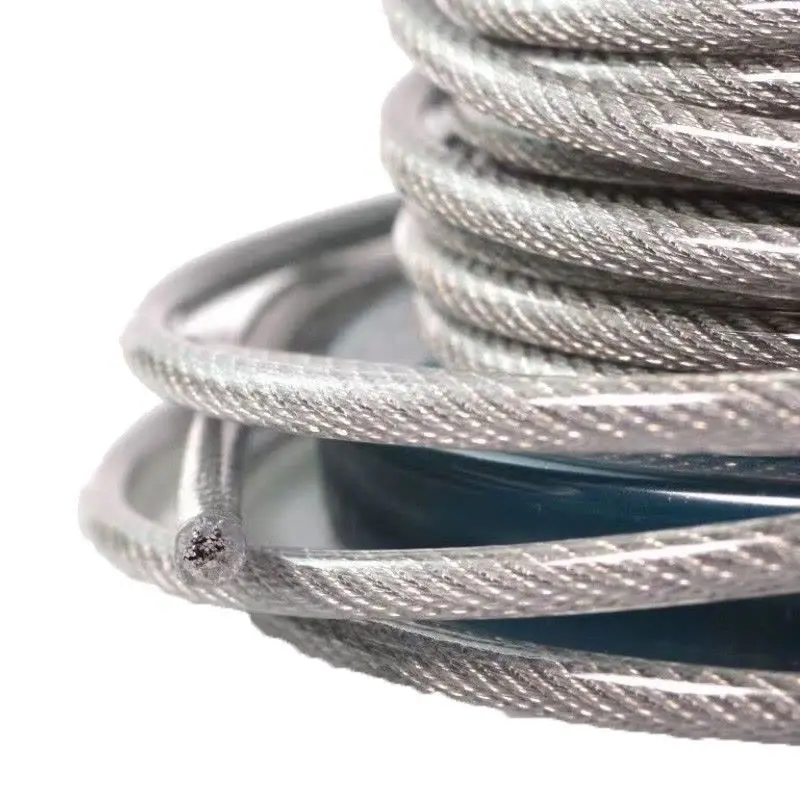
(2) Outer Sheath (Polymer Coating): Physical Isolation and Safety Assurance
The outer sheath refers to a layer of polymer material (usually PVC or nylon) wrapped around the outside of the steel cable after stranding. It is an added physical protective layer.
Representative Technologies: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), Nylon (Polyamide).
Core Functions: Provides physical isolation, visual identification, reduces friction with contact surfaces, prevents minor impacts, and enhances handling safety and comfort.
Application Scenarios: Suitable for areas in contact with the human body, aesthetically pleasing environments, or indoor and semi-indoor environments requiring protection of sensitive structural surfaces.
Conclusion: Surface treatment is fundamental to ensuring the structural integrity of steel cables is protected from chemical abrasion; the outer sheath provides additional physical protection and safety features.
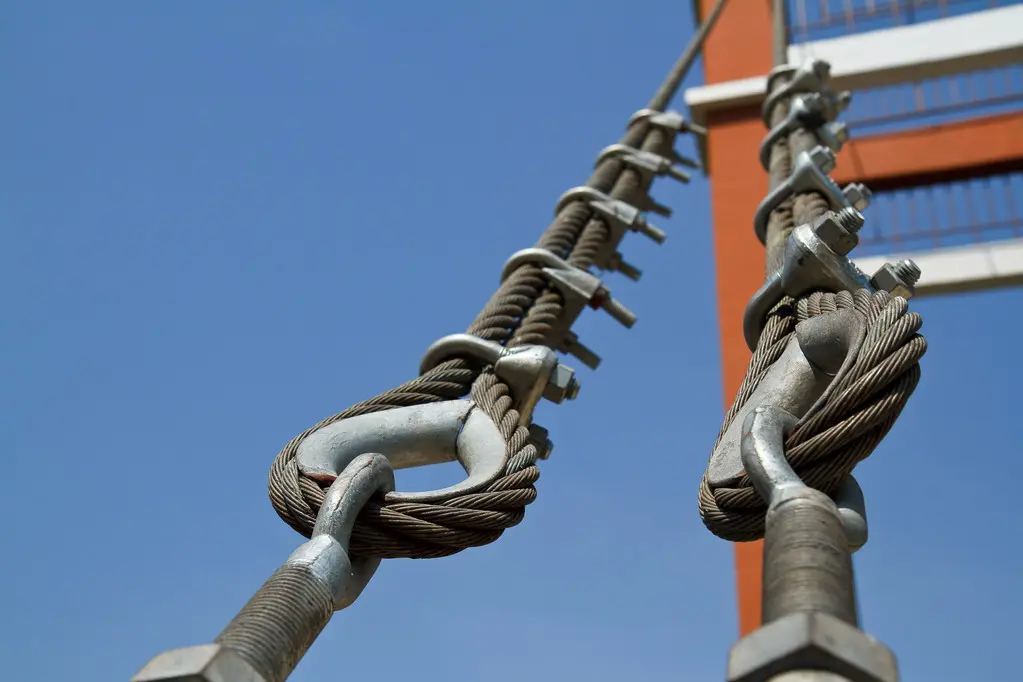
2. Key Scenarios for Mandatory Use of Sheathed Steel Cables
In certain specialized applications, the use of outer sheathed steel cables is not merely an optimization, but a prerequisite for ensuring safety and functionality. The sheath forms an insulating barrier, effectively preventing direct contact between the steel core and the external environment.
Applications Requiring Sheathed Cables:
Protecting Sensitive or Delicate Structures: For example, in the suspension and fixation of glass curtain walls, lightweight roofs of high-end buildings, or artistic installations, the sheath prevents the steel wires from scratching and damaging the contact surfaces.
In applications involving human-computer interaction: For any application where people may have direct contact, such as fitness equipment, park facilities, children's playgrounds, or public artwork, sheathing significantly reduces the risk of abrasions, pinching, or contact injuries.
Aesthetic and functional requirements of indoor environments: In commercial or residential interior design, sheathed cables help enhance aesthetics while providing basic electrical and thermal insulation.
3. Finish Performance Comparison: Galvanized Steel Cable vs. Stainless Steel Cable The two most common surface treatments—galvanizing and stainless steel—each have their advantages, and their suitability depends on the severity of environmental corrosion and project cost considerations.
| Feature Comparison | Galvanized Steel | Stainless Steel, 304/316 |
| Corrosion resistance level | Medium to good. Suitable for general outdoor and intermittently humid environments. | From good to excellent. Performs exceptionally well in highly corrosive environments. |
| Working principle | The zinc layer provides sacrificial anode protection and is preferentially corroded. | The chromium oxide layer forms a self-healing passivation film, completely isolating corrosive media. |
| Environmental restrictions | The protective lifespan is shorter in high salinity/high acidity/alkalinity environments. | Excellent durability, suitable for harsh industries such as marine, chemical, and pharmaceutical. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Optimal. Low initial investment, suitable for applications with low requirements for chemical resistance. | The cost is relatively high. However, its extremely long lifespan and low maintenance requirements result in a better total life cycle cost. |
Please note: Regardless of whether galvanized or stainless steel finish is used, a PVC or nylon outer sheath can be added to achieve a dual layer of protection and safety.
Professional Guidance: Customized Steel Cable Selection Service
We understand that every project is unique. Correct steel cable selection is a complex process involving technical standards, environmental analysis, and long-term cost accounting.
Our technical team is dedicated to assisting clients in making the best choice based on the following key dimensions:
Industry specifications and technical standards compliance.
The corrosiveness of the actual operating environment (temperature, humidity, salinity, chemical exposure).
The project's comprehensive requirements for safety, durability, maintenance frequency, and aesthetics.
The required mechanical properties and load-bearing capacity.
Through detailed technical manuals, sample demonstrations, and on-site survey support, we ensure that clients receive not only high-quality products, but also an efficient and long-lasting solution that perfectly meets their specific needs.