What you need to know about the selection and application of smooth steel wire rope
Selection and Applications of Bright Steel Wire Ropes

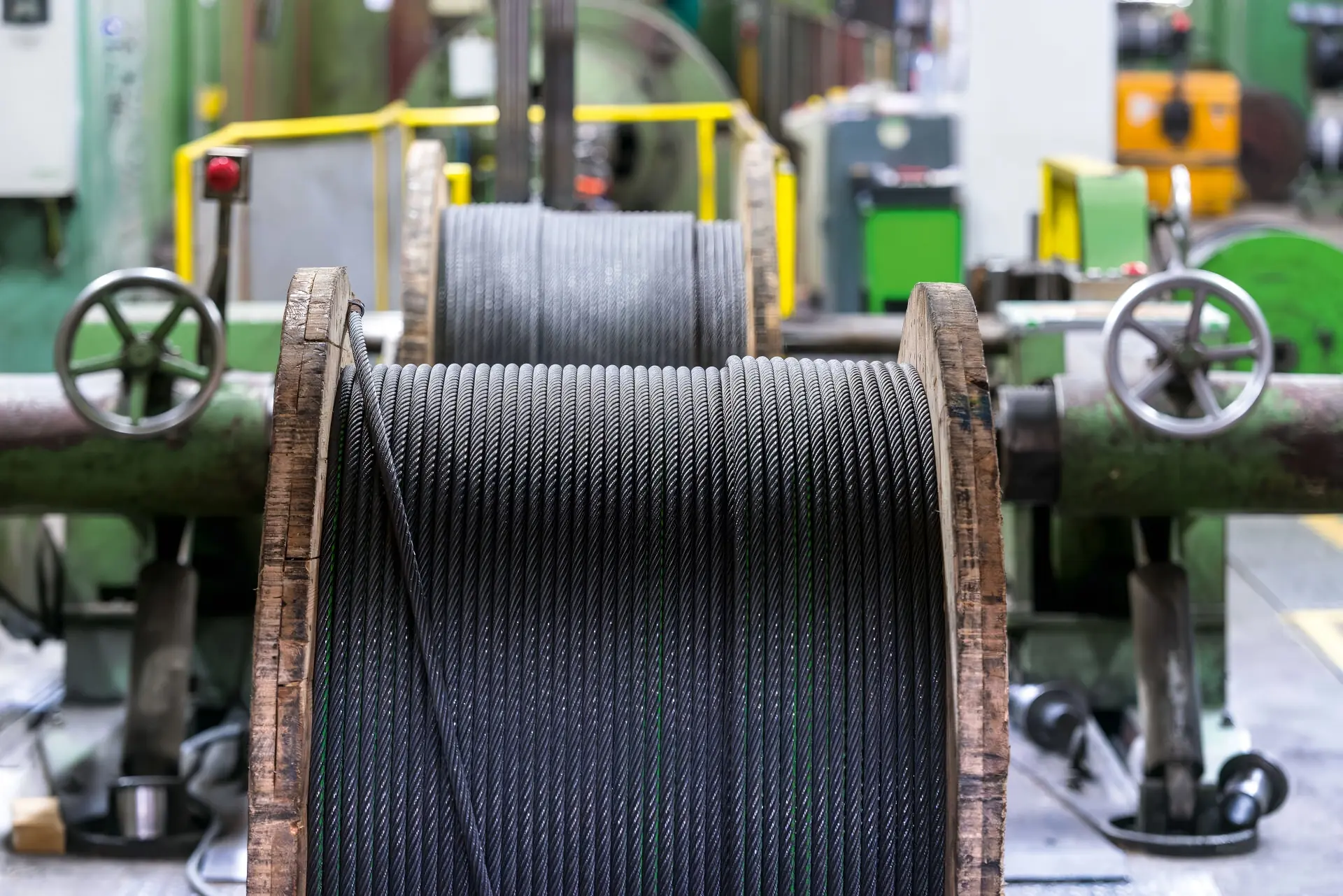
Bright steel wire ropes typically refer to steel wire ropes that have not undergone surface treatments such as galvanizing or plastic coating, directly exposing the original color and smoothness of the steel. With their high strength, excellent wear resistance, and compact structure, they play a crucial role in many engineering fields.
This article will delve into the key selection factors for bright steel wire ropes and detail their main applications.
I. Key Selection Factors for Bright Steel Wire Ropes
The selection of bright steel wire ropes is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it must be comprehensively considered based on the specific application conditions, load characteristics, and environmental conditions. The following are some of the most important determining factors:
1. Construction: Balancing Flexibility and Wear Resistance
The structure of a steel wire rope is usually expressed as the number of strands × the number of wires per strand, which is the core factor determining its performance.
| Structure type | Describe | Features | Typical applications |
| 6x7 | 6 strands, each with 7 steel wires | It has strong wear resistance and a compact structure, but poor flexibility. | Cableways, traction cables, and fixed cables are used in applications where flexibility is not a primary concern. |
| 6x19 | 6 strands, each with 19 steel wires | It has a balanced structure with moderate flexibility and abrasion resistance. | Cranes, hoists, and bridge cables are the most widely used applications. |
| 6x37 | 6 strands, each with 37 steel wires | It has high flexibility and can better adapt to frequent bending fatigue, but its wear resistance is slightly inferior. | Ship loading and unloading, winches, and other applications requiring high bending fatigue resistance. |
2. Twisting Direction and Lay: Affects Rotation Resistance and Lifespan
(1) Regular Lay: The twist direction of the wires within the strand is opposite to the twist direction of the strand in the rope.
Features: Stable rope structure, good rotation resistance, easy to inspect.
Applications: Most lifting and hoisting applications.
(2) Lang's Lay: The twist direction of the wires within the strand is the same as the twist direction of the strand in the rope.
Features: Larger contact area, better abrasion resistance and bending fatigue resistance, but poorer rotation resistance and more prone to unraveling.
Applications: Mining hoists requiring frequent bending and high abrasion resistance, drum winding, etc.
3. Core Type: Affects Strength and Support Capacity
The core is crucial to the structural stability, flexibility, and lubricant storage capacity of the wire rope.
(1) Fiber Core (FC/Hemp Core): Typically made of hemp or synthetic fibers.
Features: ,Optimal flexibility, can store a large amount of lubricating oil.
Applications: Applications with low load requirements or high flexibility requirements.
(2) Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC): The core itself is a wire rope.
Features: High strength, provides excellent radial support to the rope body, strong resistance to extrusion deformation, and high temperature resistance.
Applications: Cranes and lifting equipment with high loads, high temperatures, and multi-layer winding.
4. Wire Strength Grade: The basis of load-bearing capacity.
When selecting wire rope, it is essential to ensure that the tensile strength of its wires (e.g., 1770MPa, 1960MPa, 2160MPa, etc.) meets the minimum breaking strength requirement of the application. Higher strength results in greater load-bearing capacity, but usually, flexibility will decrease accordingly.
5. Lubrication: The lifeline of bright wire ropes. Bright wire ropes must have sufficient lubricant at the factory to reduce friction between the internal wires and improve resistance to bending fatigue and corrosion. Since bright wire ropes lack a protective coating, regular and adequate in-service lubrication is crucial for extending their service life.
II. Main Applications of Bright Steel Wire Ropes
Bright steel wire ropes, due to their high strength and compact structure, are widely used in the following fields:
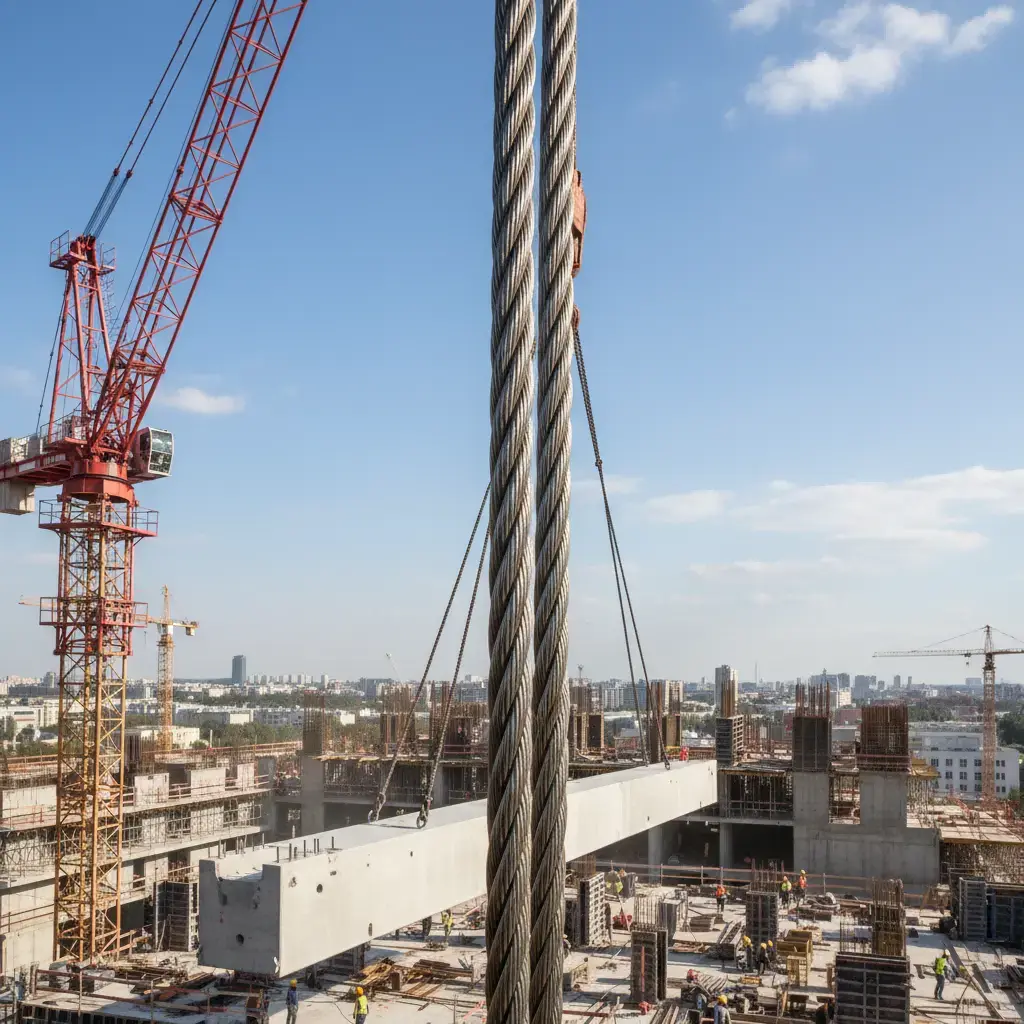
1. Lifting & Hoisting
This is the core application area for bright steel wire ropes.
(1) Applications: Main hoisting and luffing wire ropes for bridge cranes, gantry cranes, tower cranes, electric hoists, etc.
(2) Reasons for Selection: Industrial hoisting environments place extremely high demands on the breaking strength and abrasion resistance of ropes. The high strength of bright ropes, combined with an IWRC core, provides the necessary support and load-bearing capacity.
2. Mining
(1) Applications: Mine hoists, inclined shaft traction, coal mine scraper conveyors, etc.
(2) Reasons for Selection: Mine hoisting places extremely stringent requirements on the safety factor, bending fatigue, and abrasion resistance of ropes. High tensile strength Lange lay structures are often selected to maximize service life and safety. 3. Ports & Ships
(1) Applications: Port gantry cranes, loader/unloaders, marine cranes, etc.
(2) Reasons for selection: Frequent lifting and lowering operations are required. Although the marine environment is highly corrosive, for ropes requiring extremely high strength or those that will be frequently replaced, smooth ropes may still be chosen, supplemented with special anti-corrosion grease.
4. Traction & Anchoring
(1) Applications: Cable car (cable car) load-bearing and traction cables, bridge cables, temporary or permanent anchoring cables for large structures.
(2) Reasons for selection: In these applications, wire ropes typically need to withstand continuous, stable high tensile forces, and structural stability and fatigue resistance are primary considerations, highlighting the high strength advantage of smooth ropes.
Summary: Advantages and limitations of smooth ropes
| Features | Advantages | Limitation |
| Strength | For the same diameter, it can usually provide a higher minimum breaking tensile force. | A compact structure may sacrifice some flexibility. |
| Cost | Compared to galvanized or stainless steel ropes, the initial purchase cost is lower. | / |
| Anti-corrosion | Lack of surface coating (such as zinc plating or plastic coating). | It has poor corrosion resistance and is not suitable for long-term exposure to humid, acidic, alkaline, or high-salt spray environments. |
| Maintain | Strict and regular lubrication maintenance is required. | Improper maintenance can easily lead to internal corrosion and fatigue failure. |